A proper cold room installation is more than just building a cold box; it’s about creating a precisely controlled environment that protects the value and safety of your perishable goods. Whether you’re in the food, pharmaceutical, or horticultural industry, a reliable cold room is the backbone of your operation. Poor cold storage infrastructure contributes to staggering losses, with some studies showing 40 to 50% of fresh produce going to waste.
This guide walks you through every critical step of the cold room installation process, from the initial sketch to the final performance test. We’ll break down the technical details into simple, understandable terms to show you what a professional installation looks like.
Phase 1: Planning and Design
Getting the foundation right, both literally and figuratively, starts here. Rushing the planning phase is a recipe for costly mistakes and an inefficient cold room.
Planning and Site Assessment
Before a single panel is ordered, a thorough site assessment is the first crucial step. A professional installer will evaluate the intended location to ensure it’s suitable. This involves:
Accessibility: Can delivery trucks, forklifts, and staff move around the area easily?
Structural Integrity: Can the floor support the immense weight of the cold room, its shelving, and a full inventory of products?
Ventilation: Is there enough space around the future condenser unit for it to dissipate heat effectively? A stuffy room can choke the refrigeration system.
Utilities and Drainage: Is there adequate electrical power available? And is there a place for defrost and cleaning water to drain away safely without pooling?
A detailed site check prevents expensive modifications down the line and is a hallmark of a professional cold room installation. For multi-room or warehouse-scale projects, see our cold-chain warehouse guide.
Design and Equipment Selection
With a viable site confirmed, the focus shifts to designing the cold room itself. This is where your specific needs shape the project. Key decisions include:
Sizing: The room must be large enough for your maximum expected inventory, with extra space for airflow.
Temperature Range: Are you building a chiller (around 0 to 5 °C), a freezer (around -20 °C), or a blast freezer for rapid cooling (down to -40 °C)? This choice affects everything from insulation thickness to the type of refrigeration machinery needed. If you’re unsure which is right for you, read our guide on blast chiller vs. blast freezer.
Cooling Load Calculation: Engineers calculate the total heat the refrigeration system needs to remove. A standard freezer might require around 75 watts of cooling power per cubic meter, but this is adjusted for factors like door openings and ambient heat. The refrigeration unit is then sized to handle a bit more than this peak load to avoid running at 100% capacity all the time.
Component Choice: Modern installations favor eco friendlier refrigerants like R448A or R134a to comply with environmental laws. In hot climates like South India, it’s crucial to select components like high-ambient refrigeration units that can perform reliably even when outdoor temperatures soar.
For a system perfectly matched to your business, it’s best to work with a manufacturer like F-Max Systems that can customize every component for your local conditions.
Layout Design
The internal layout of your cold room directly impacts its efficiency. A smart layout balances storage density with the need for uniform air circulation. You can’t just pack it to the gills. Planners focus on:
Airflow Paths: Stored items should never obstruct the flow of cold air from the evaporator (the unit cooler). Leaving a small gap between products and the walls is essential to prevent hot spots.
Shelving: Using open or wire style shelving rather than solid shelves helps cold air reach every item. The arrangement of shelves and pallets can dramatically affect temperature uniformity throughout the room.
Aisles and Doors: The layout must allow for easy movement of people and equipment while minimizing the time the door stays open.
Phase 2: Site, Foundation, and Utility Preparation
With a solid plan, the physical work begins. Preparing the site and foundation correctly is non negotiable for a long lasting and effective cold room installation.
Site Preparation
This stage involves getting the physical location ready for construction. The area is cleared, cleaned, and made safe for the installation crew. The single most important task is ensuring the floor is perfectly level and smooth. An uneven base can cause panels to misalign, creating gaps that compromise insulation and structural integrity. Installers will often mark the exact footprint of the cold room on the floor to guide the assembly.
Building a Solid Foundation
The foundation for a cold room does more than just support its weight; it provides a critical thermal barrier. For freezer rooms operating below 0 °C, this is especially important to prevent a destructive phenomenon called frost heave. Frost heave occurs when moisture in the ground freezes and expands, which can crack and buckle the floor from below.
To prevent this, a proper foundation includes:
A strong, reinforced concrete slab.
A vapor barrier (a thick plastic sheet) to block ground moisture.
Layers of rigid insulation boards to stop the cold from reaching the soil.
For freezers, low wattage heating cables or pipes are often embedded in the foundation to keep the ground temperature just above freezing.
Utilities (Power and Services)
A cold room is hungry for power. A reliable electrical supply is its lifeline. Most commercial cold rooms require a three phase power supply to run their compressors and fans. For critical applications like vaccine or pharmaceutical storage, a backup power source like a standby generator or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is essential.
Other utilities include:
Lighting: Energy efficient LED lighting is the standard, as it produces very little heat and performs well in cold temperatures.
Drainage: A drain line is needed to carry away water from the evaporator during defrost cycles.
Water Supply: If the room requires regular washdowns, a nearby water connection is necessary.
Getting Ventilation Right
Ventilation is a two part concept in any cold room installation.
External Ventilation: The condensing unit, which is typically located outside, expels a lot of heat. It needs to be in a well ventilated area so that hot air can dissipate. Poor ventilation can cause the system to overheat and perform poorly.
Internal Air Circulation: Inside the cold room, the evaporator fans must circulate cold air evenly to maintain a uniform temperature. Proper circulation prevents warm pockets and ensures all products are kept at the correct temperature.
Phase 3: The Build (Assembling the Insulated Structure)
This is where the cold room starts to take physical shape. The quality of the panel assembly determines the thermal efficiency of the entire structure.
Assembling the Insulated Panels
Modern cold rooms are built using prefabricated sandwich panels (PUF panels). These panels have a core of rigid foam insulation (typically polyurethane or PUF) with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.024 W/m·K, sandwiched between metal sheets.
They are joined together using cam lock mechanisms embedded in the edges. Installers use a special key to turn these locks, which pulls the panels tightly together for a secure, airtight fit. This modular system makes the cold room installation process incredibly fast and allows the room to be disassembled and relocated if needed.
Floor, Wall, and Ceiling Panel Installation
The assembly process follows a logical sequence:
Floor Installation: For rooms with an insulated floor, panels are laid on the prepared level base. For heavy duty applications, a more common method involves laying insulation boards on top of a vapor barrier and then pouring a reinforced concrete floor over them.
Wall Installation: Wall panels are set into a channel on the floor and locked to one another, one by one. Installers ensure each panel is perfectly vertical and that corners are square.
Ceiling Installation: Ceiling panels are lifted and placed on top of the walls, resting in a notch designed for this purpose. For large rooms, the ceiling may need extra support from a suspension system or internal beams to prevent sagging.
Door Installation
The door is the most used component and a potential weak point for heat leaks. A professional cold room installation includes fitting a heavily insulated door with high quality gaskets to create an airtight seal. Freezer doors often have heater wires in the frame to prevent the gasket from freezing shut.
Crucially, every cold room door must have an internal safety release mechanism. This allows anyone inside to open the door, even if it’s locked from the outside, preventing accidental entrapment.
Sealing and Final Insulation Touches
The final step of the build is to seal every single joint and penetration. Installers apply flexible silicone sealant to all interior panel seams, corners, and junctions. Any hole made for pipes, wiring, or mounting bolts is meticulously sealed with grommets, foam, and sealant to prevent air and moisture from getting in. A perfectly sealed room is the key to energy efficiency and preventing messy frost buildup.
Phase 4: Refrigeration System Setup
With the insulated box built, it’s time to install the cooling machinery that makes it all work.
Mounting the Unit Cooler (Evaporator)
The unit cooler, or evaporator, is the component that sits inside the cold room and blows the cold air. It’s usually mounted high on a wall or ceiling. Its placement is strategic; it must be positioned to circulate air throughout the entire space without being blocked by shelving or products. A good rule is to leave a gap between the unit and the wall that is at least as large as the unit’s own thickness, ensuring free air movement.
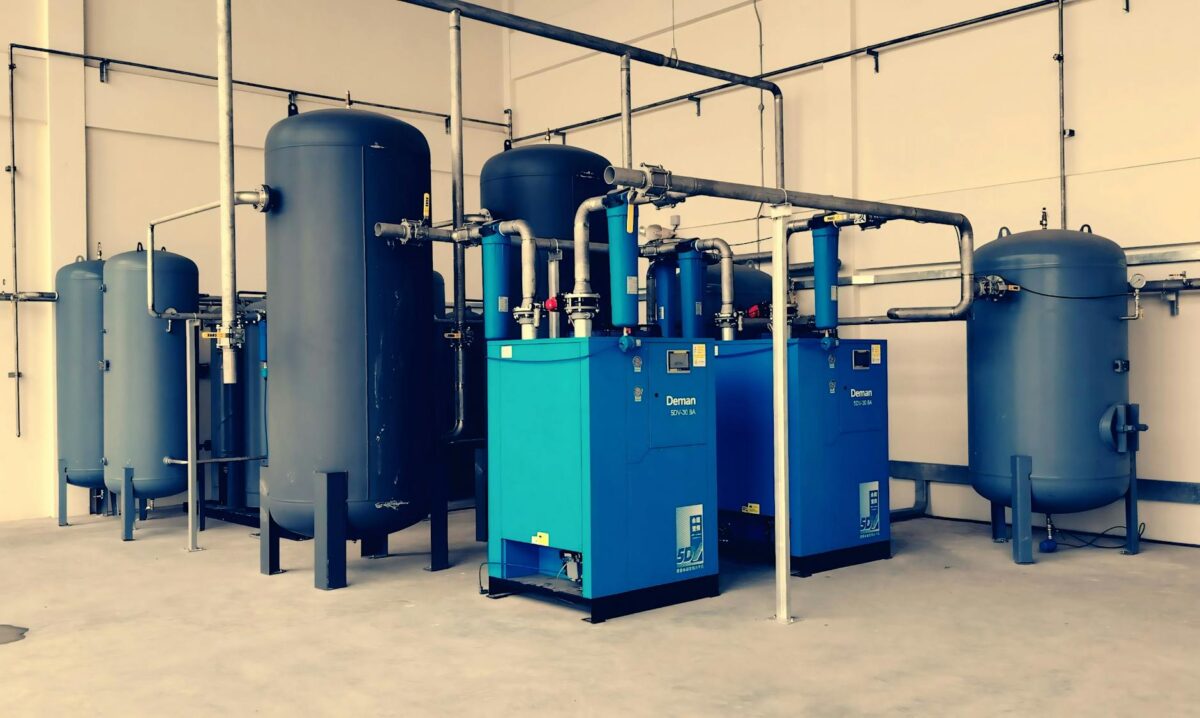
Installing the Refrigeration Unit (Condenser)
The condensing unit, containing the compressor and condenser coil, is the heart of the system and is usually located outside. It should be placed on a solid, level surface like a concrete pad and fitted with vibration isolators to reduce noise and wear. It’s vital to leave plenty of space around the unit for maintenance access and unrestricted airflow. For a custom solution designed to handle the high heat of an Indian summer, you can explore specialized condensing units.
Connecting the Refrigeration Piping
Copper pipes connect the indoor and outdoor units, forming a closed loop for the refrigerant to travel. This part of a cold room installation requires precision.
Pipe Sizing: Pipes must be the correct diameter to ensure efficient refrigerant flow without causing a significant pressure drop.
Cleanliness and Brazing: Pipes are cut cleanly and joined by brazing (a form of high temperature soldering). This is done while flowing dry nitrogen through the pipes to prevent scale from forming inside.
Traps and Slopes: The suction line pipe is often installed with a slight slope and special “P traps” to ensure lubricating oil, which circulates with the refrigerant, makes it back to the compressor.
Power Distribution and Electrical Wiring
A qualified electrician connects all the components. This involves running a dedicated power circuit to the system, installing a central control panel with a thermostat and safety devices, and wiring the lights and fans. All wiring inside the cold room uses moisture and cold resistant cables, and any penetrations through the panels are sealed completely. Vapor proof LED light fixtures are standard for safety and efficiency.
Phase 5: Finalizing, Testing, and Commissioning
The cold room is built, but the job isn’t done. The final phase involves a series of rigorous tests to ensure everything works perfectly before you start loading your valuable products.
Setting Up Shelving and Storage
How you arrange storage inside the room matters. Best practices include using corrosion resistant, open wire shelving to promote airflow. It’s important to leave a gap of a few inches between stored goods and the walls and to avoid stacking products so high that they block the evaporator fans. A good rule of thumb is to keep items at least 6 inches off the floor for hygiene and circulation.
Refrigerant Charging
After a thorough leak test, the system is charged with the correct type and amount of refrigerant. Technicians use a digital scale to add refrigerant by weight. An incorrect charge, either too much or too little, can lead to poor performance, high energy consumption, and even compressor damage. The global cold storage capacity reached 719 million cubic meters in 2020, and every one of those spaces relies on a precise refrigerant charge to function.
Performing Leak and Pressure Tests
Before charging, the entire piping system is pressurized with an inert gas like dry nitrogen and left for 24 hours to ensure it is completely leak free. Even the tiniest leak can cause the system to lose refrigerant over time, leading to a loss of cooling.
Verifying with a Temperature Uniformity Test
This test, also called temperature mapping, confirms that the temperature is consistent throughout the entire cold room. Multiple calibrated temperature sensors are placed in various locations (corners, center, near the door) to log data over 24 to 72 hours. This identifies any hot or cold spots, which can then be corrected by adjusting airflow or storage layout.
Testing and Commissioning
Commissioning is the final quality check. The installation team performs a complete operational test, including:
Pull Down Test: Measuring how long it takes for the room to cool from ambient temperature down to its setpoint.
Control Verification: Testing that the thermostat correctly cycles the compressor on and off.
Safety Checks: Verifying that the internal door release, alarms, and any other safety features are working perfectly.
Defrost Cycle Test: Ensuring the defrost system for the evaporator works correctly.
Once all tests are passed, the cold room installation is complete, and the team will provide you with documentation and training on how to operate your new system. When you need a reliable cold room installation built to the highest standards, it’s essential to partner with experienced professionals.
Best Practices for a Flawless Cold Room Installation
To summarize, a successful project adheres to several key best practices:
Hire Certified Professionals: Never cut corners on labor. Experienced technicians are crucial for a reliable and long lasting system.
Thorough Testing: A complete commissioning process, including leak tests and temperature mapping, and ongoing preventive maintenance of cold rooms, is non negotiable.
Prioritize Sealing: Every joint, corner, and penetration must be perfectly sealed to maintain thermal integrity and efficiency.
Design for Maintenance: Leave adequate space around machinery for future servicing.
Focus on Safety: Ensure all safety features, especially the internal door release and alarms, are installed and tested.
By following these guidelines, you ensure your cold room will perform optimally, protect your inventory, and provide a solid return on your investment for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cold Room Installation
What is the first step in a cold room installation?
The very first step is comprehensive planning and site assessment. Before any construction, a professional team evaluates the location for structural soundness, accessibility, power availability, and proper ventilation to ensure the site can support the cold room.
How long does a cold room installation take?
The timeline varies depending on the size and complexity of the project. However, thanks to modern modular panels with cam lock systems, the physical assembly of a standard walk in cooler can often be completed in just a few days. Custom builds or large warehouses will naturally take longer.
Why is floor insulation so important for a freezer room?
Floor insulation is critical in freezers to prevent “frost heave.” This is a destructive process where cold penetrates the ground, freezes any moisture in the soil, and causes the expanding ice to crack and lift the concrete floor from beneath. Insulated foundations with vapor barriers and sometimes heating cables prevent this.
What kind of lighting is best for a cold room?
Vapor proof LED lights are the industry standard. They are highly energy efficient, produce very little heat (which reduces the cooling load), perform reliably in cold temperatures, and are sealed to protect against moisture.
Can I move my cold room after it has been installed?
Yes, if your cold room was constructed with modular insulated panels using a cam lock system. One of the main advantages of this type of construction is that the panels can be unlocked, disassembled, moved to a new location, and reassembled.
How do you ensure a cold room is airtight?
Airtightness is achieved through meticulous sealing. After assembling the panels, installers apply flexible silicone sealant to all interior joints, corners, and floor to wall junctions. Every penetration for pipes, wires, or bolts is also sealed with grommets and sealant to eliminate any path for air leakage.